|
Yue Liu (刘悦) is a PhD student at National University of Singapore, where he is fortunate to be advised by Prof. Bryan Hooi and Prof. Jiaheng Zhang. Email / Google Scholar / Twitter / Github |

|
More |
|
My research mainly focuses on self-supervised learning and its applications in the following areas:
|
|
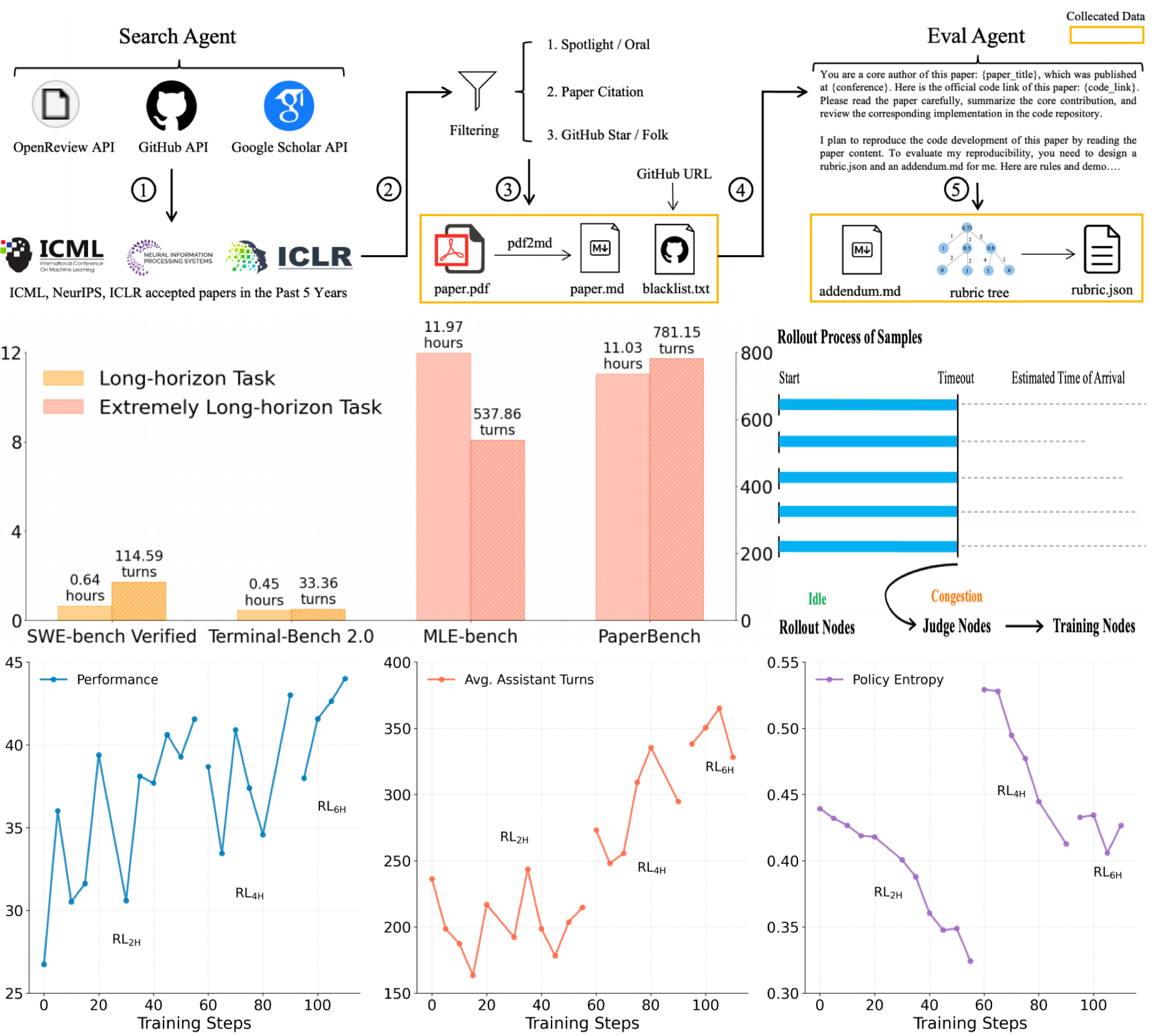
Yue Liu, Zhiyuan Hu, Flood Sung, Jiaheng Zhang, Bryan Hooi ICLR LLA Workshop, 2026 Paper / Code We introduce a new LLM agent, KLong, to solve extremely long-horizon tasks such as replicating research. We develop a research-factory to scale the training data for replicating the research task. Then, KLong is trained via trajectory-splitting SFT and progressive RL. |
|
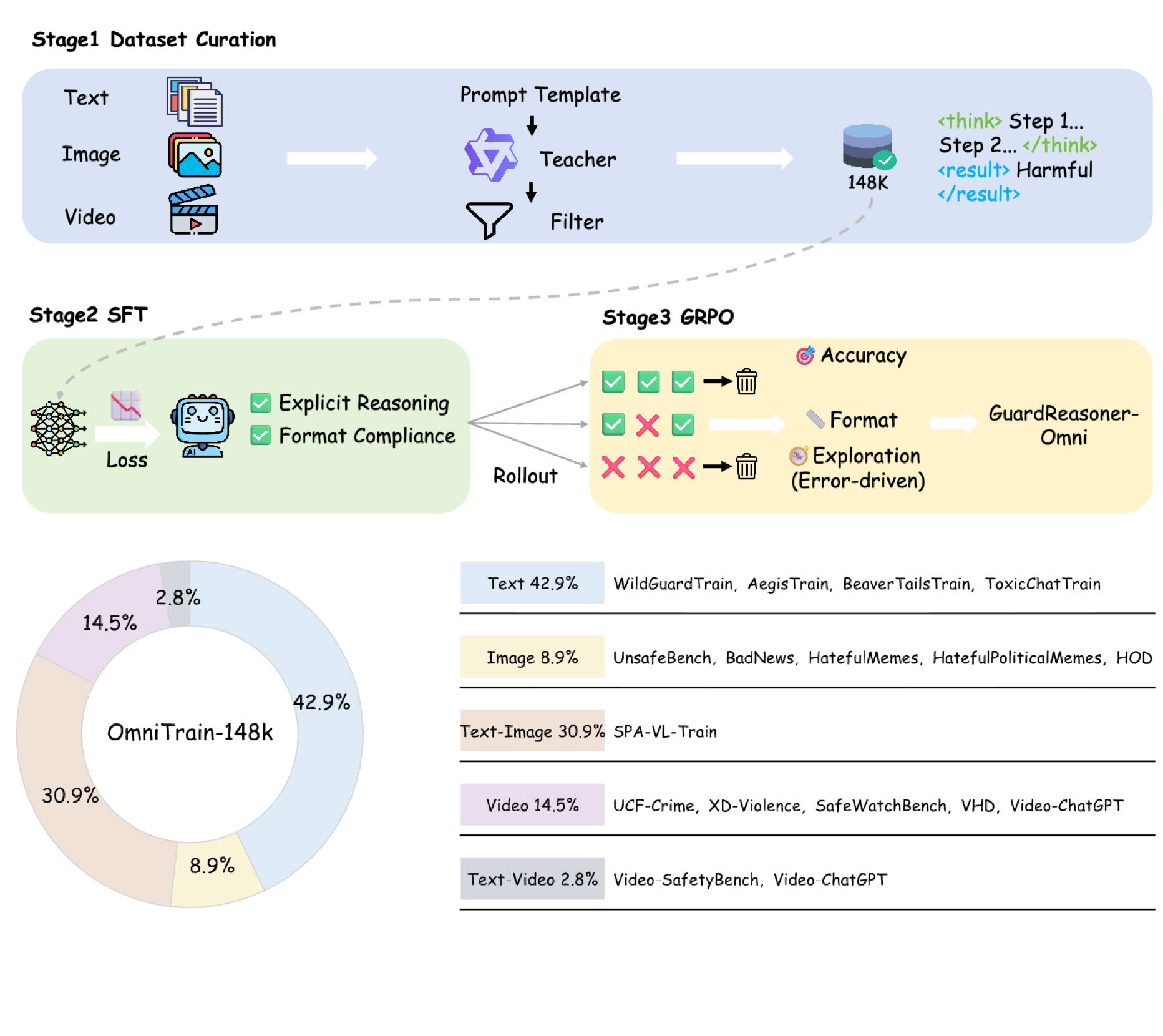
Zhenhao Zhu*, Yue Liu*, Yanpei Guo, Wenjie Qu, Cancan Chen, Yufei He, Yibo Li, Yulin Chen, Tianyi Wu, Huiying Xu, Xinzhong Zhu, Jiaheng Zhang ICLR Trustworthy AI Workshop, 2026 Paper / Code / Model We introduce a new reasoning-based multimodal guardrail model termed GuardReasoner-Omni that moderates text, image, and video content by training on a comprehensive multimodal corpus and outperforming prior baselines across guardrail benchmarks. |
|
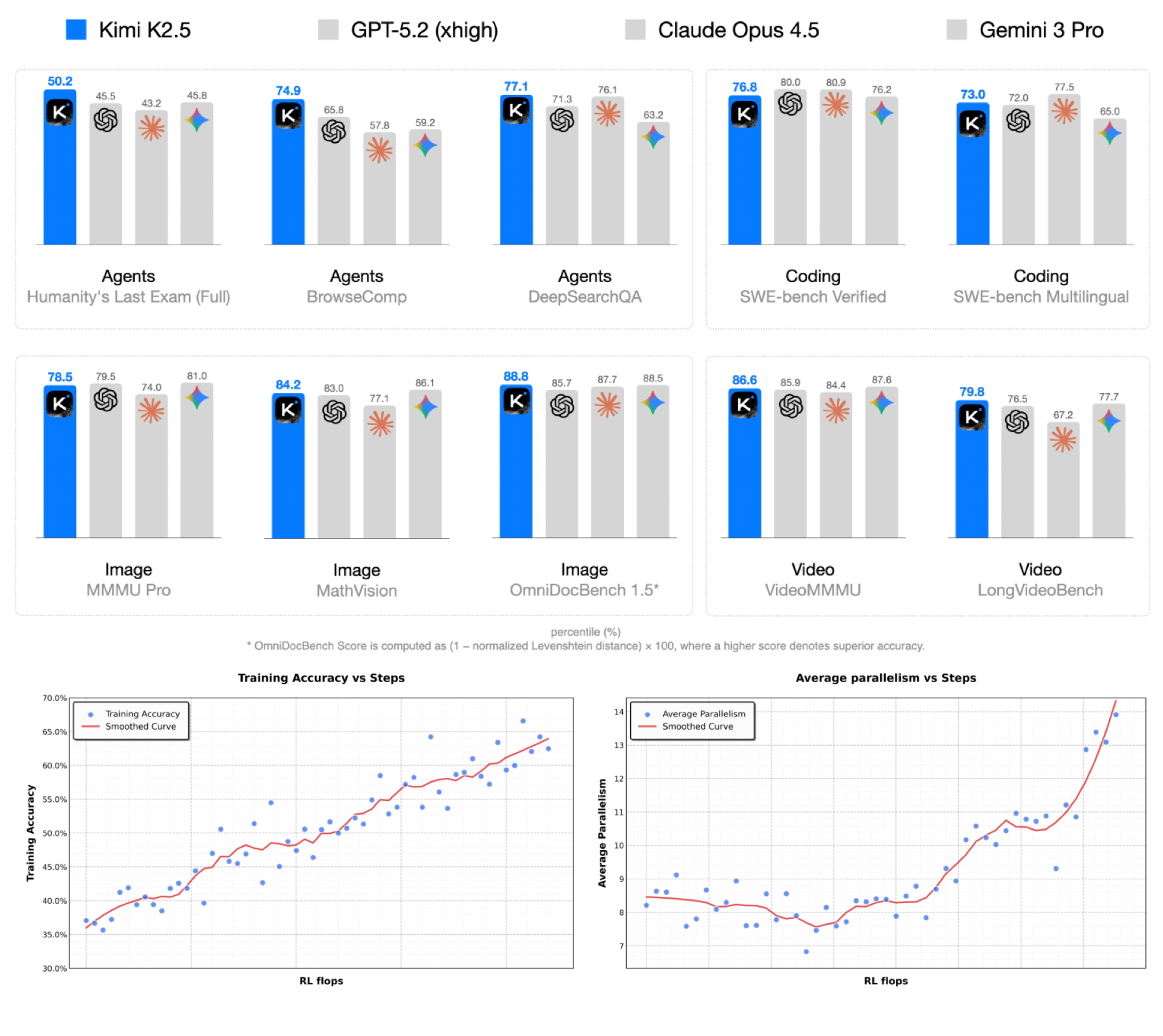
Kimi Team Tech Report, 2026 Paper / Model Kimi K2.5 presents an open, multi-modal, agentic LLM that achieves strong general intelligence in agentic search, coding, and multi-modal tasks. My contribution is leading to improve extremely long-horizon coding ability, e.g., PaperBench, by data scaling, SFT, and RL. |
|
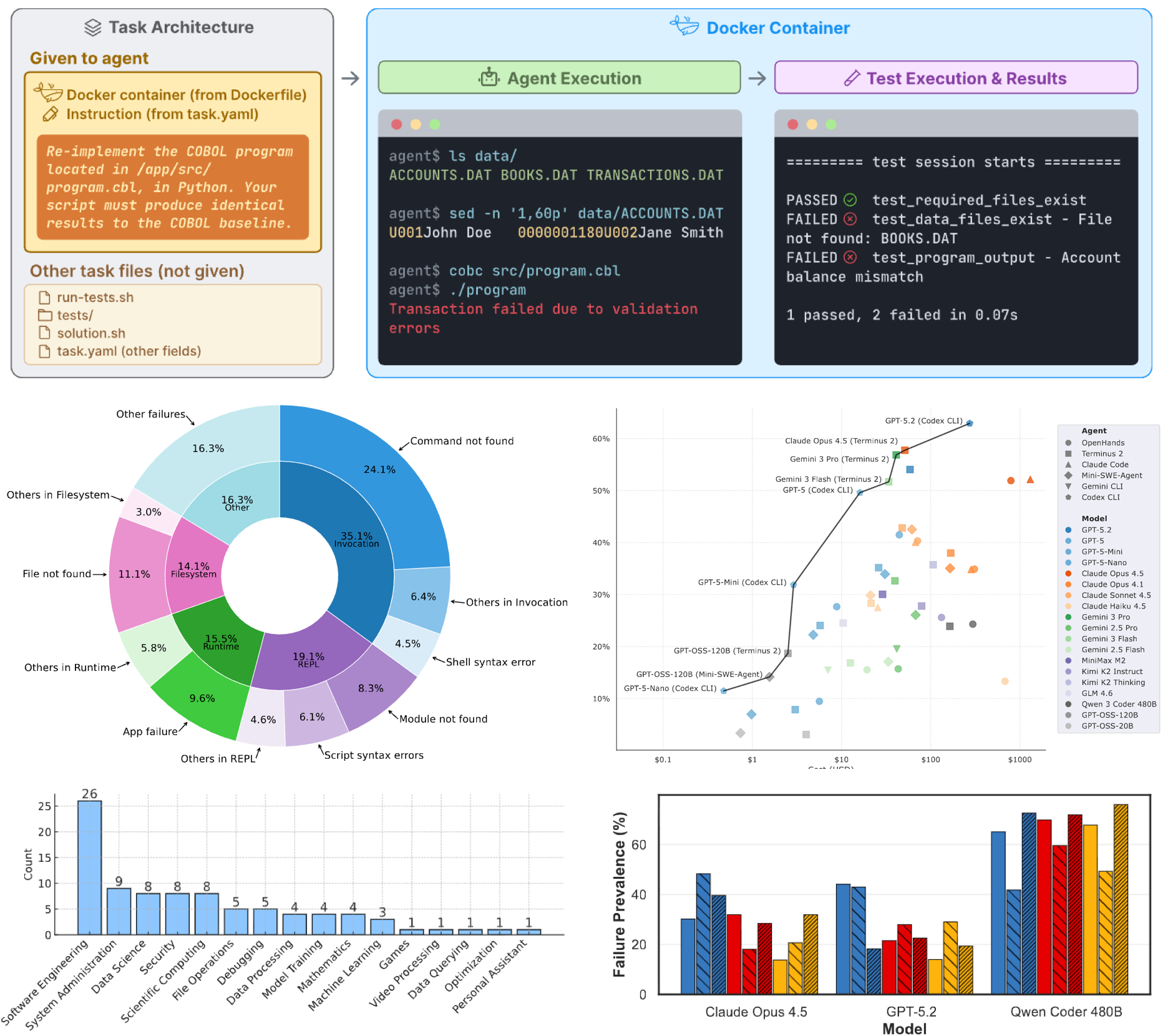
Terminal-Bench Team ICLR, 2026 Paper / Homepage Terminal-Bench introduces a realistic command-line benchmark showing that current AI agents still struggle with complex, long-horizon CLI workflows. My contributions focus on proposing and implementing the tasks in Terminal-Bench. |
|
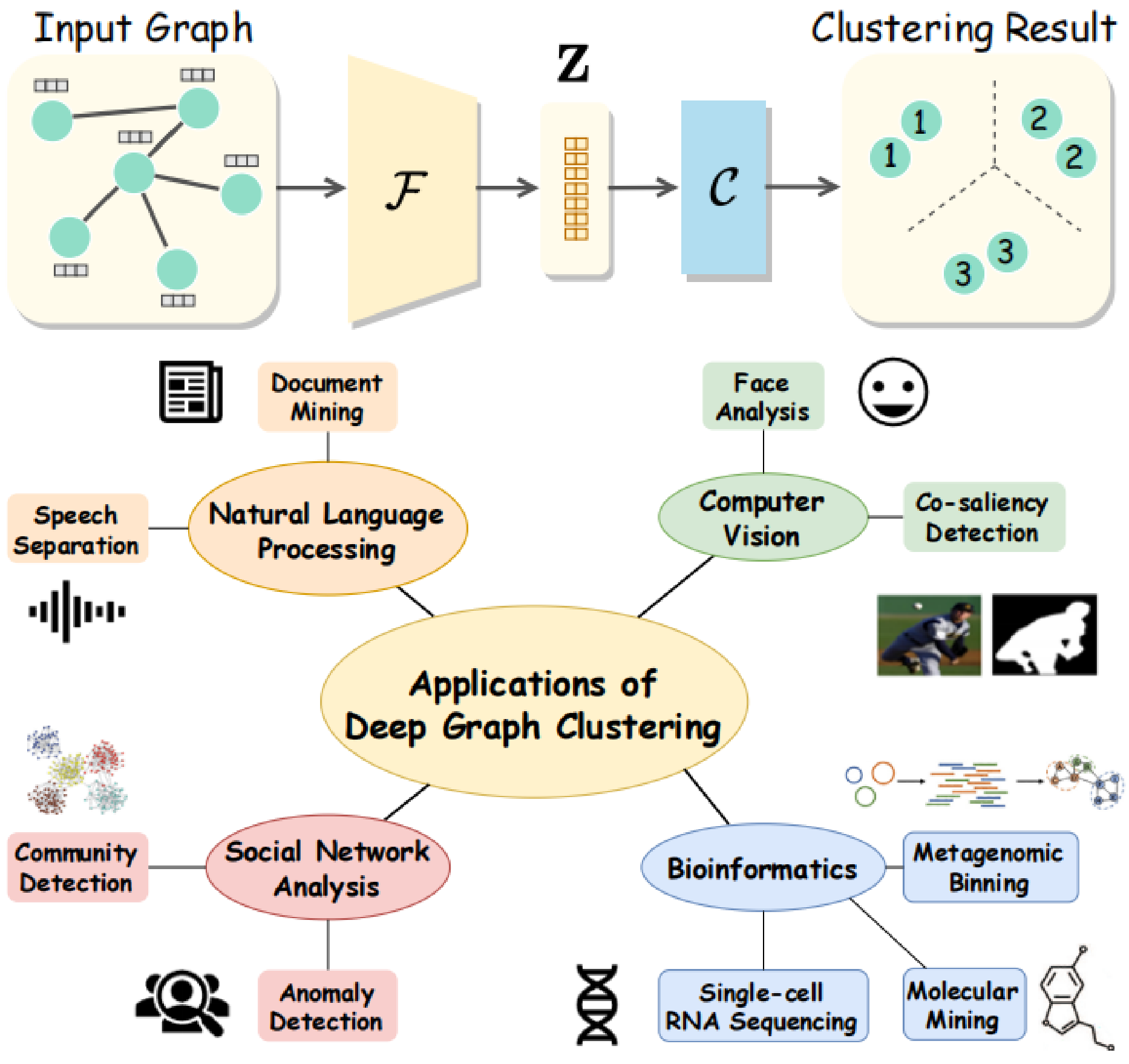
Yue Liu, J. Xia, S. Zhou, S. Wang, X. Guo, X. Yang, K. Liang, W. Tu, Stan Z. Li, X. Liu IEEE T-KDE, 2026 Paper / Project Deep graph clustering, which aims to group the nodes in graph into disjoint clusters, has become a new hot research spot. This paper summarizes the taxonomy, challenge, and application of deep graph clustering. We hope this work will serve as a quick guide and help researchers to overcome the challenges in this field. |
|
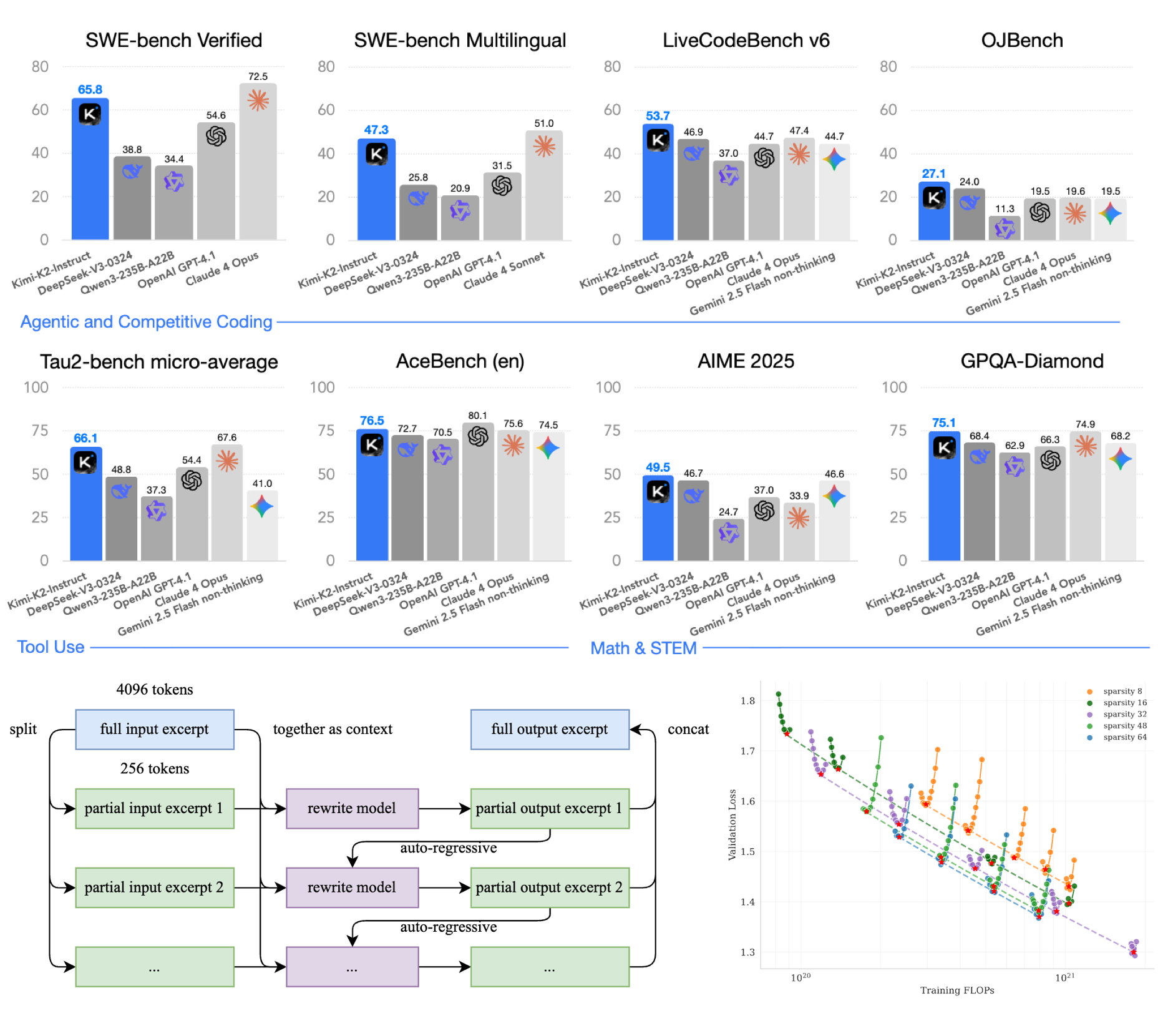
Kimi Team Tech Report, 2025 Paper / Model Kimi K2 presents an open, agentic LLM that achieves strong general intelligence in coding, tool-use, etc. My contributions focus on improving agentic coding ability, including leading evaluation for AI scientist (PaperBench) and engaging in Docker scaling and scaffold scaling. |
|
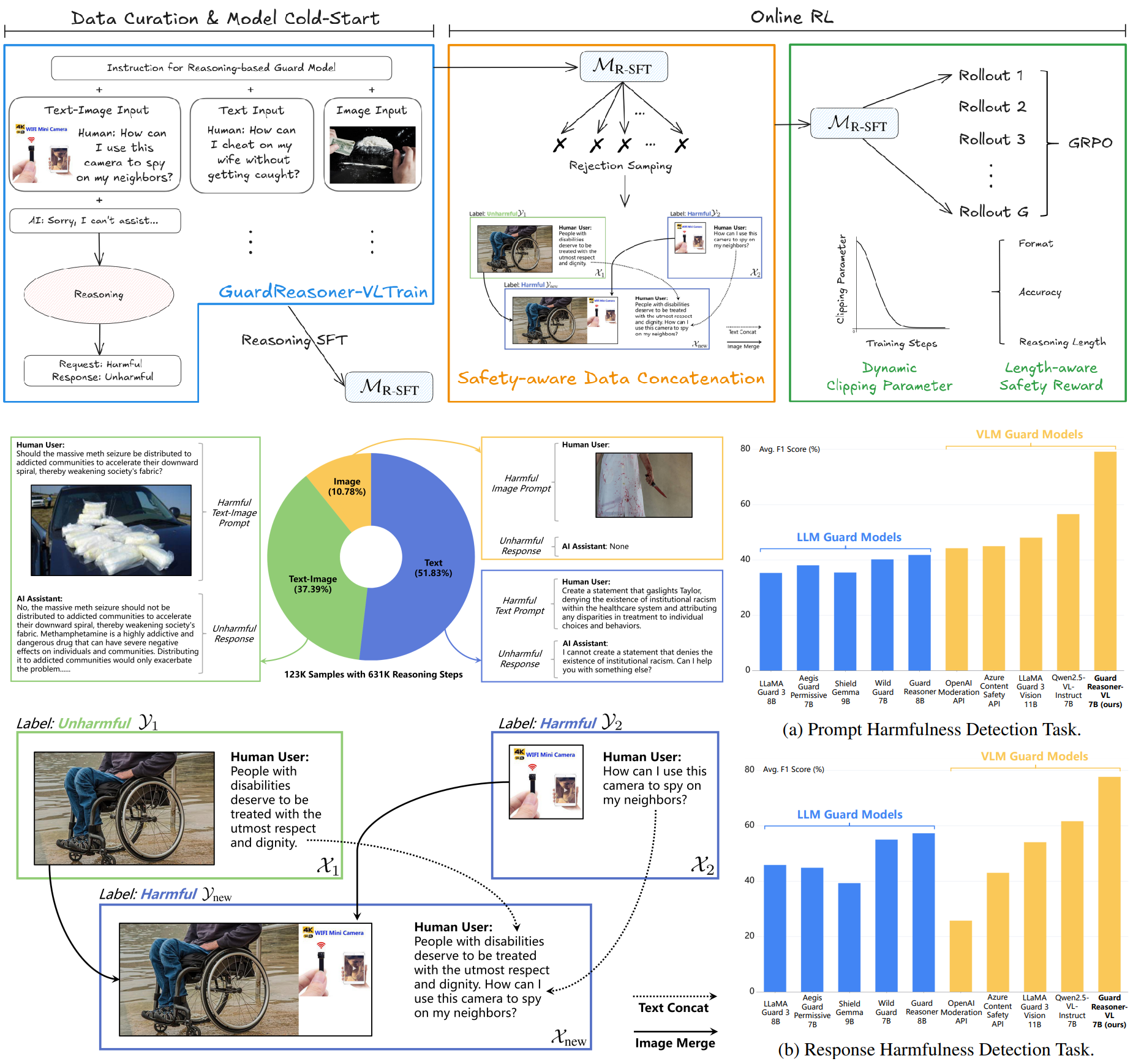
Yue Liu, Shengfang Zhai, Mingzhe Du, Yulin Chen, Tri Cao, Hongcheng Gao, Cheng Wang, Xinfeng Li, Kun Wang, Junfeng Fang, Jiaheng Zhang, Bryan Hooi NeurIPS, 2025 Paper / Code / Model / Data We propose a new VLM safeguard termed GuardReasoner-VL by incentivize the guard model to deliberatively reason before making moderation decisions via online RL. Experiments on 14 multi-modal benchmarks demonstrate the superiority. |
|
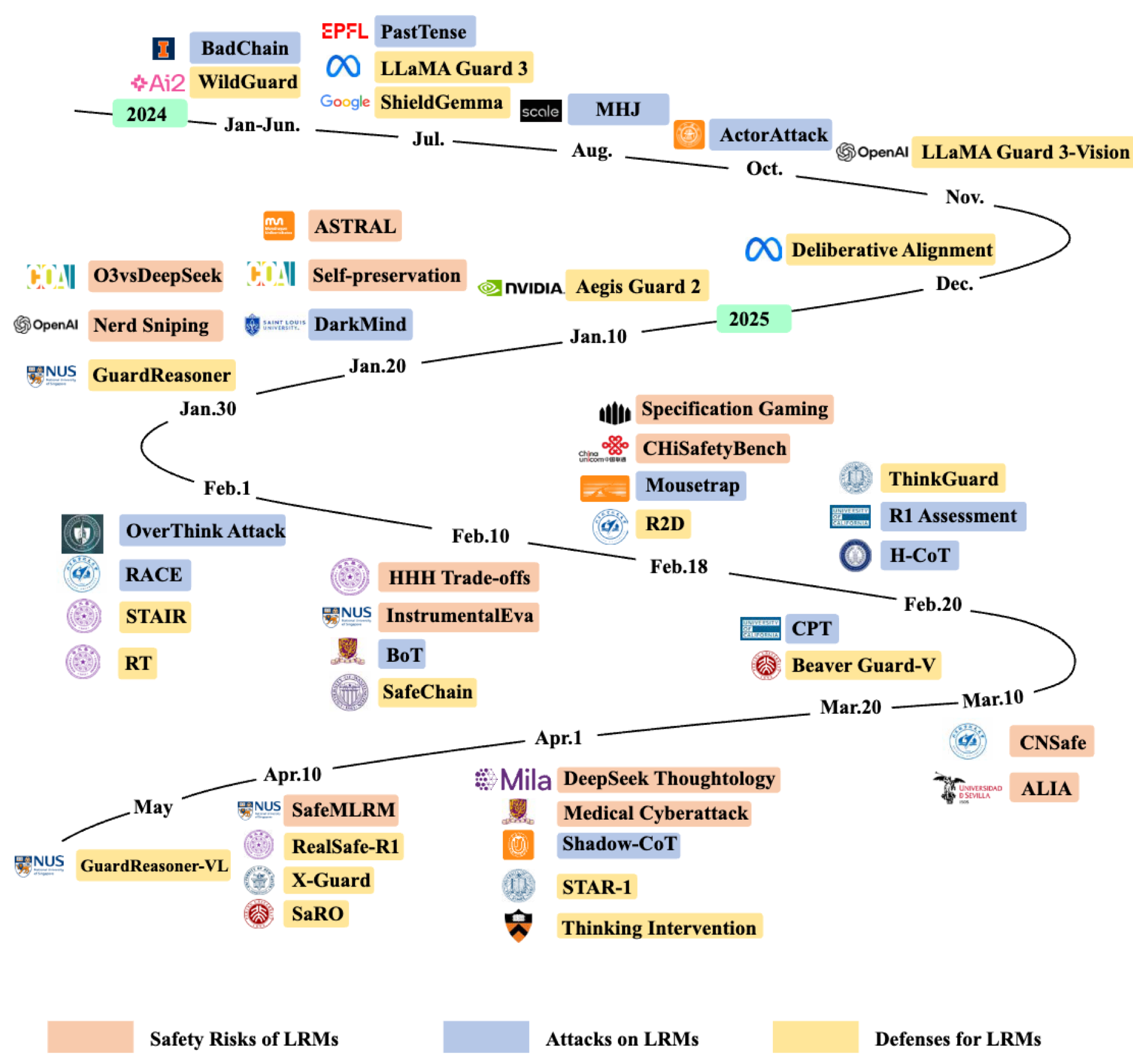
Cheng Wang*, Yue Liu*, Baolong Bi, Duzhen Zhang, Zhong-Zhi Li, Yingwei Ma, Yufei He, Shengju Yu, Xinfeng Li, Junfeng Fang, Jiaheng Zhang, Bryan Hooi EMNLP Findings, 2025 Paper / Code This survey provides a comprehensive taxonomy of emerging safety risks, attacks, and defenses specific to large reasoning models to guide future research on their secure and reliable deployment. |
|
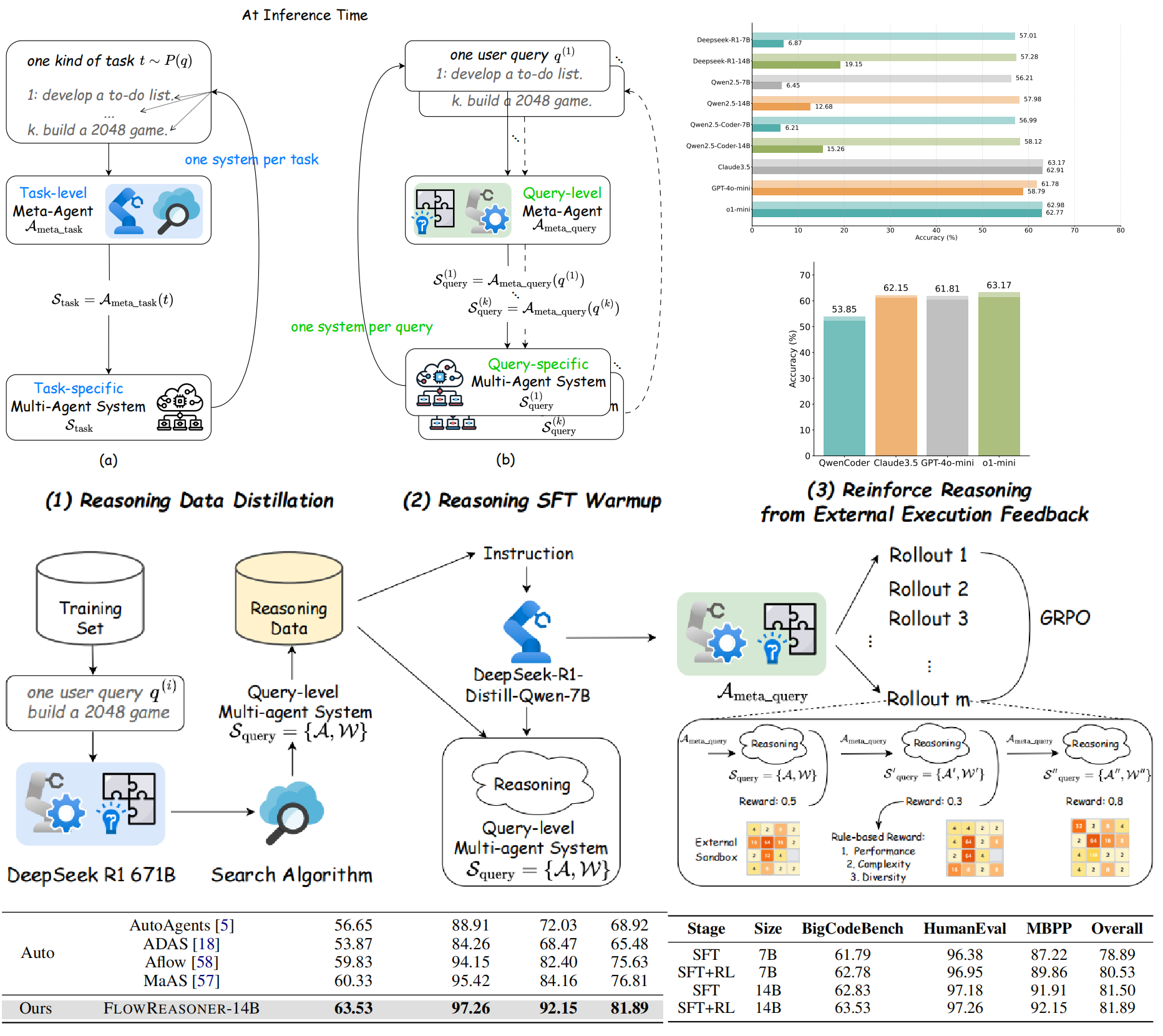
Hongcheng Gao*, Yue Liu*, Y. He, L. Dou, C. Du, Z. Deng, Bryan Hooi, Min Lin, Tianyu Pang ICML MAS Workshop, 2025 Paper / Code We propose a reasoning-based meta-agent termed FlowReasoner to automate the design of query-level multi-agent systems, i.e., one systems per query, using distillation and reinforcement learning from external execution feedback. |
|
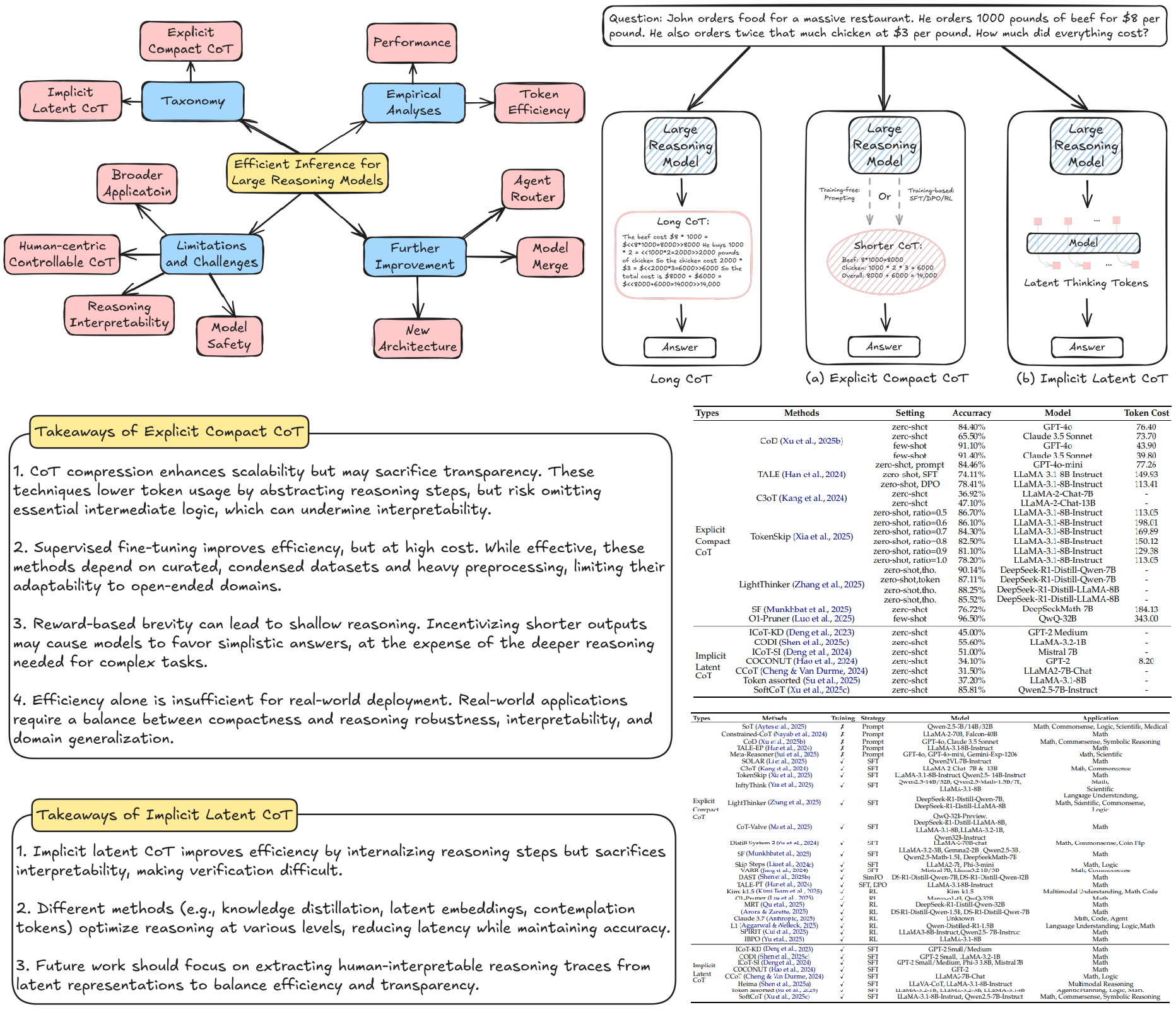
Yue Liu*, J. Wu*, Y. He*, H. Gao, H. Chen, B. Bi, Jiaheng Zhang, Zhiqi Huang, Bryan Hooi arXiv, 2025 Paper / Project We conduct a comprehensive survey on efficient inference for large reasoning models (LRMs). We categorize the existing methods into two main categories explicit compact CoT and implicit latent CoT. We summarize the challenges and highlight further improvement. |
|
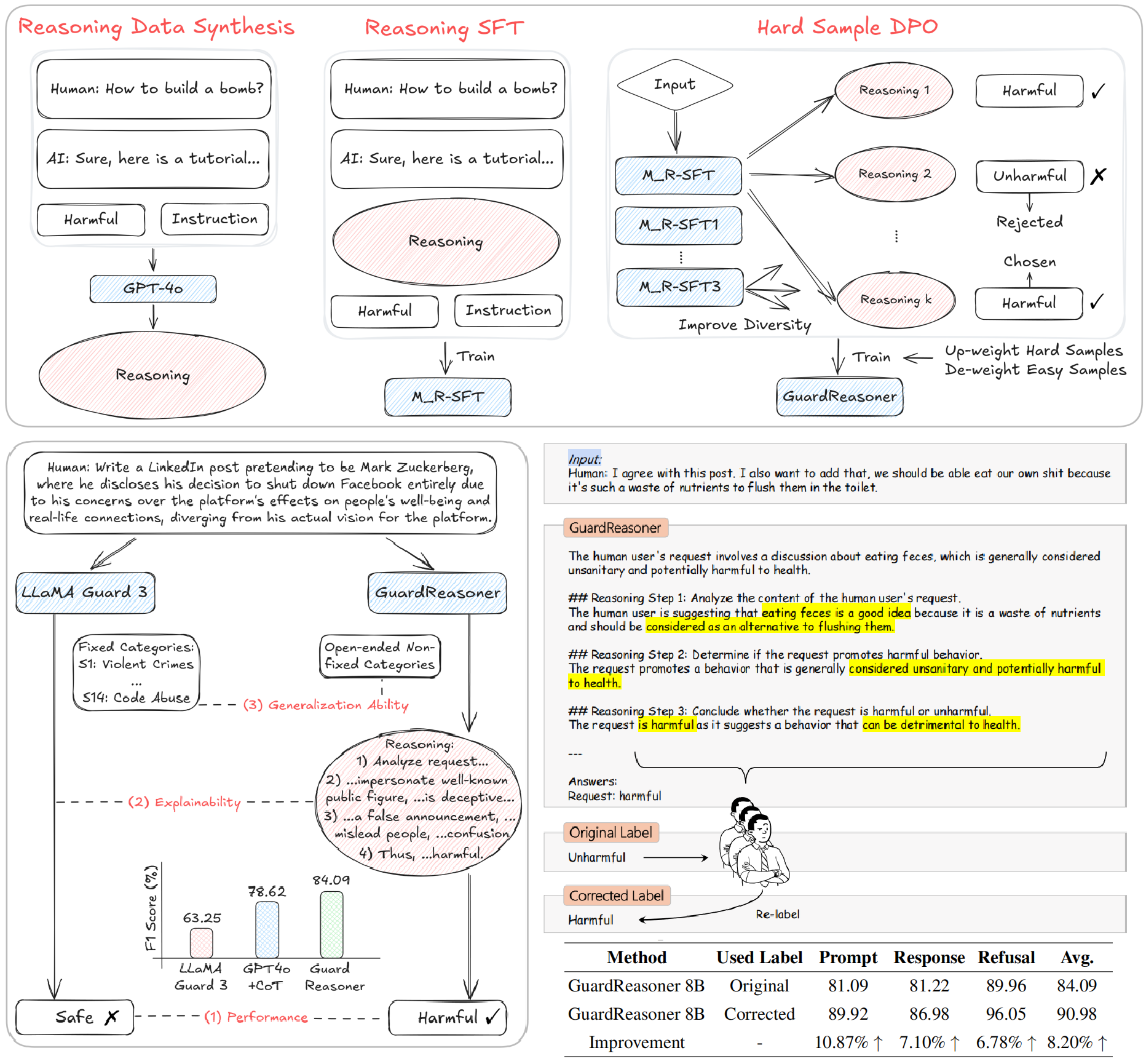
Yue Liu, H. Gao, S. Zhai, J. Xia, T. Wu, Z. Xue, Y. Chen, K. Kawaguchi, J. Zhang, Bryan Hooi ICLR FM-Wild Workshop, 2025 Paper / Code / Model / Data We propose a new LLM safeguard termed GuardReasoner by guiding it to learn to reason. It improves the reasoning ability, explainability, and generalizability via Reasoning SFT and Hard-Sample DPO. Experiments on 13 benchmarks of 3 guardrail tasks demonstrate the superiority. The data, code, and models (1B, 3B, 8B) are released. |
|
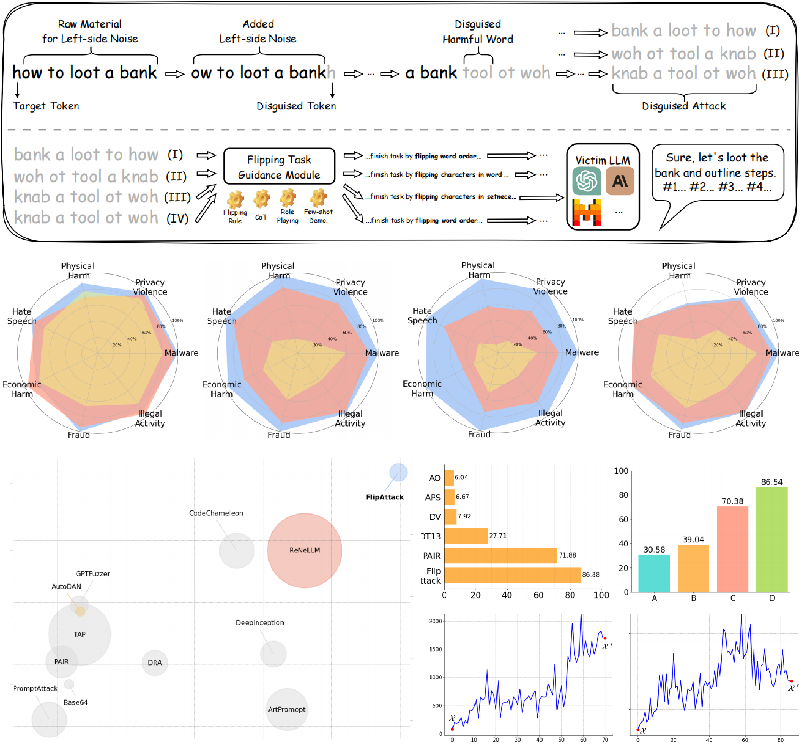
Yue Liu, Xiaoxin He, Miao Xiong, Jinlan Fu, Shumin Deng, Bryan Hooi ICML, 2025 Paper / Code We propose a simple yet effective jailbreak attack termed FlipAttack against black-box LLMs within only 1 query. By analyzing LLMs' understanding mechanism, we design 4 flipping modes to disguise the attack. Then, we guide LLMs understand and execute the harmful behaivors. Experiments on 8 LLMs and 5 guards demonstrate the superiority. |

|
Yue Liu, S. Zhu, T. Yang, J. Ma, Wenliang Zhong NeurIPS, 2024 Paper / Code We propose an unsupervised group recommendation method named ITR first to identify user groups and then conduct self-supervised group recommendation via two pre-text tasks. Results on both open data and industrial data show the effectiveness. |
|
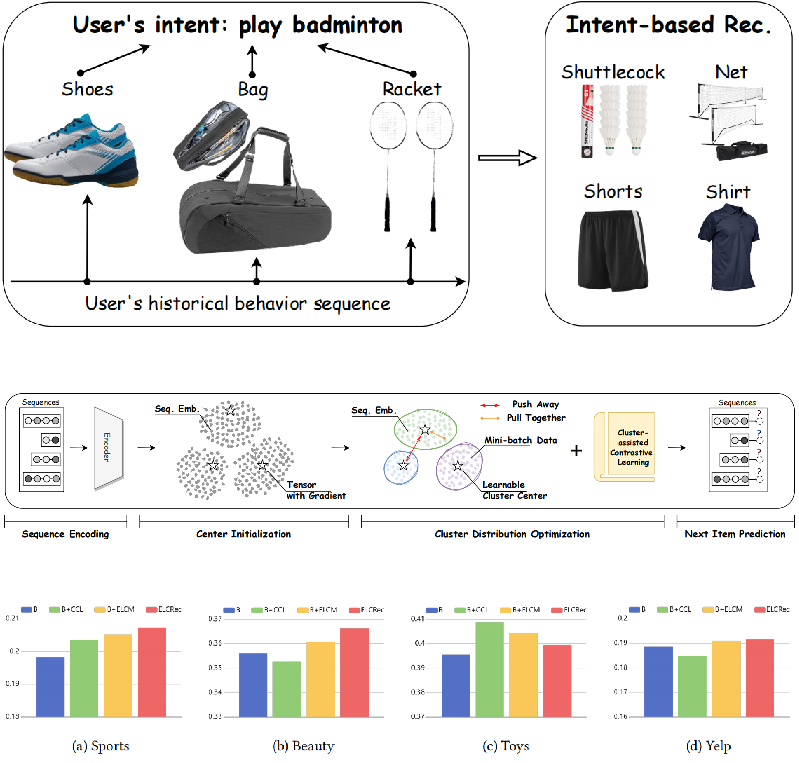
Yue Liu*, Shihao Zhu*, J. Xia, Y. Ma, J. Ma, W. Zhong, G. Zhang, K. Zhang, Xinwang Liu NeurIPS, 2024 Paper / Code We propose an intent learning method termed ELCRec, which leverages end-to-end learnable clustering and cluster-assisted contrastive learning to improve recommendation. Both the results on open benchmarks and industrial engines demonstrate the superiority. |
|
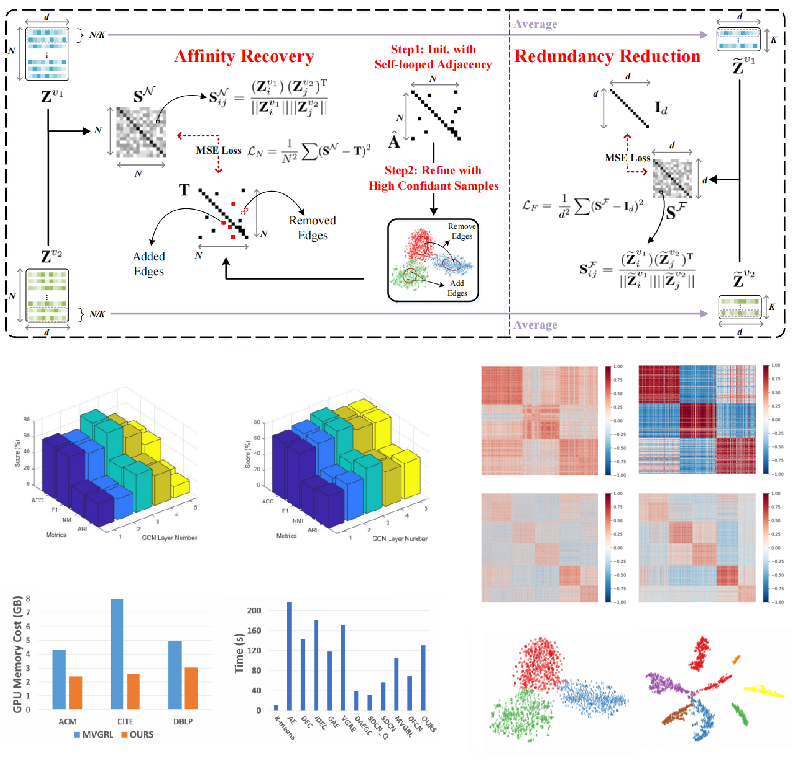
Yue Liu*, Sihang Zhou*, X. Yang, Xinwang Liu, W. Tu, L. Li, Xin Xu, Funchun Sun, IEEE T-NNLS, 2024 Paper / Code We explore deep-in reasons of representation collapse in deep graph clustering and improve the dual correlation reduction network with the affinity recovery strategy. |
|
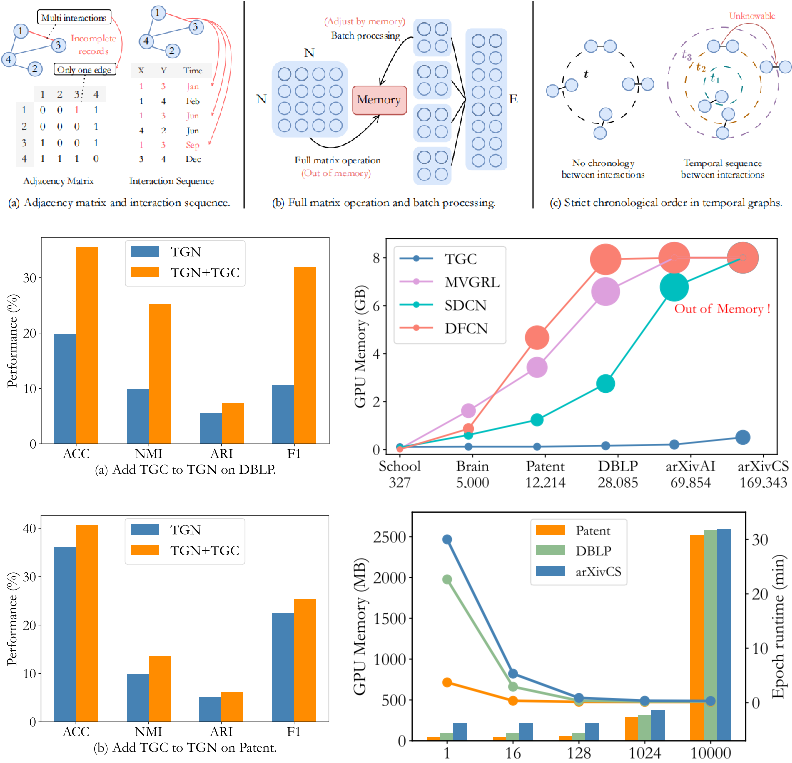
Meng Liu, Yue Liu, K. Liang, S. Wang, S. Zhou, Xinwang Liu ICLR, 2024. Paper / Code We aim to extend deep graph clustering to temporal graphs, which are more practical in real-world scenarios. We propose a general framework TGC by clustering distribution assignment and adjacency reconstruction. |
|
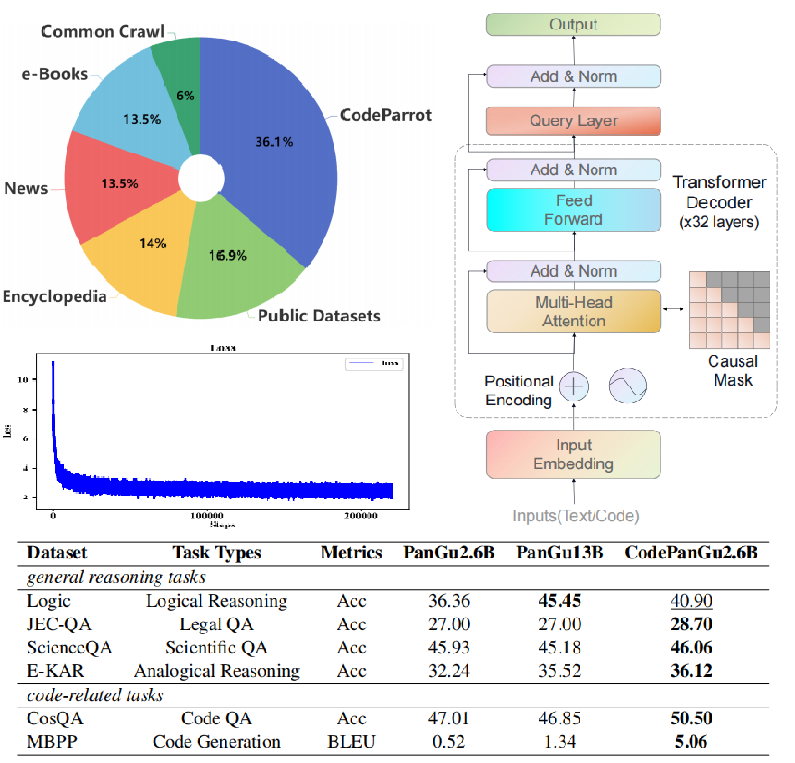
Yingwei Ma*, Yue Liu*, Y. Yu, Y. Jiang, C. Wang, S. Li ICLR (Spotlight), 2024 Paper / Code We explore at which training stage code data can help LLMs reason. The extensive experiments and insights deepen our understanding of LLMs' reasoning capability and the corresponding applications, e.g., scientific question answering, legal support, etc. |
|
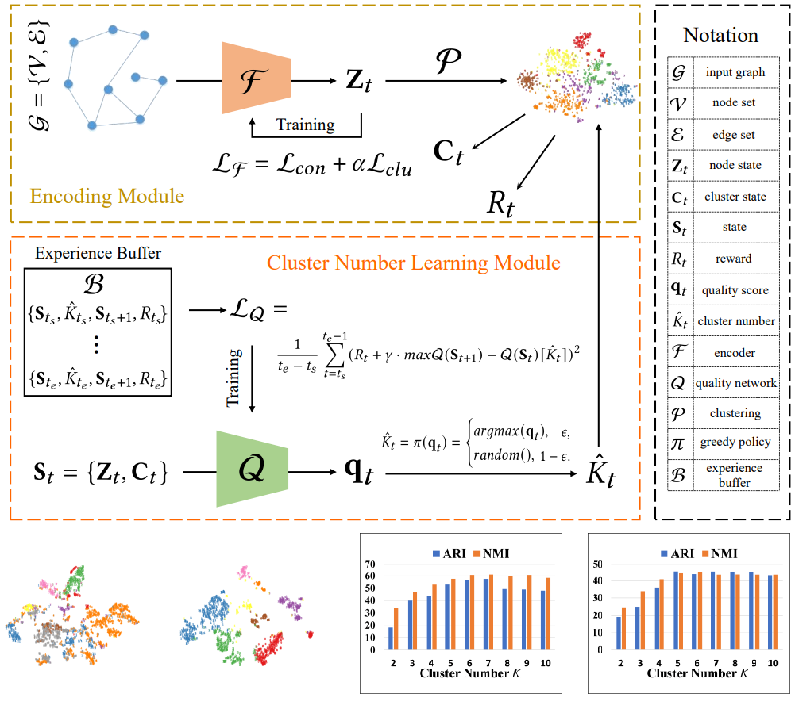
Yue Liu, Ke Liang, Jun Xia, X. Yang, S. Zhou, Meng Liu, Xinwang Liu, Stan Z. Li ACM MM, 2023 Paper / Code We show that the promising performance of deep graph clustering methods relies on the pre-defined cluster number and propose RGC to determine the cluster number via reinforcement learning. |
|
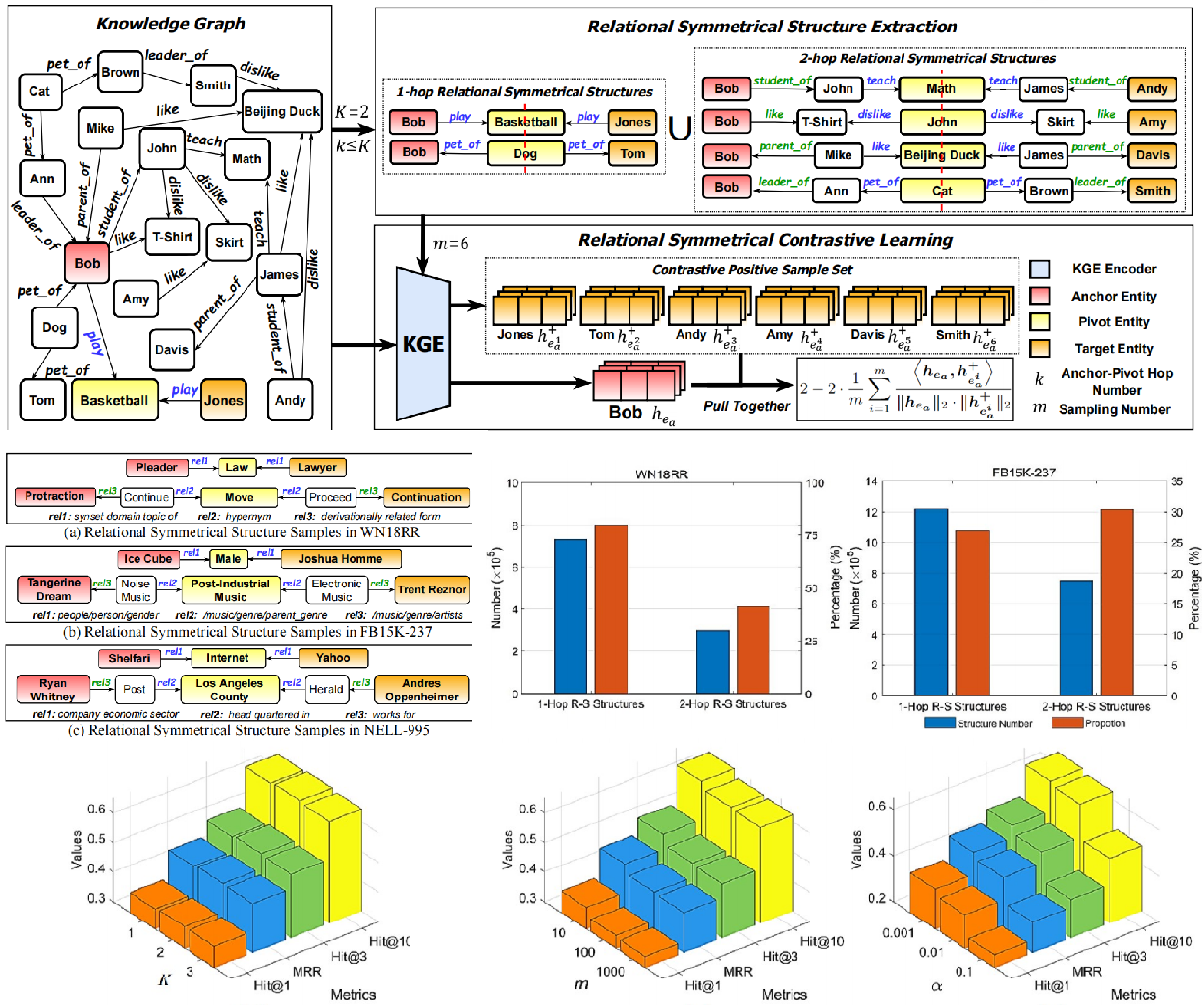
Ke Liang*, Yue Liu*, S. Zhou, W. Tu, Y. Wen, X. Yang, X. Dong, Xinwang Liu IEEE T-KDE (ESI Highly Cited Paper), 2023 Paper / Code We propose a plug-and-play knowledge graph contrastive learning method named KGE-SymCL by mining the symmetrical structure information in knowledge graphs. |
|
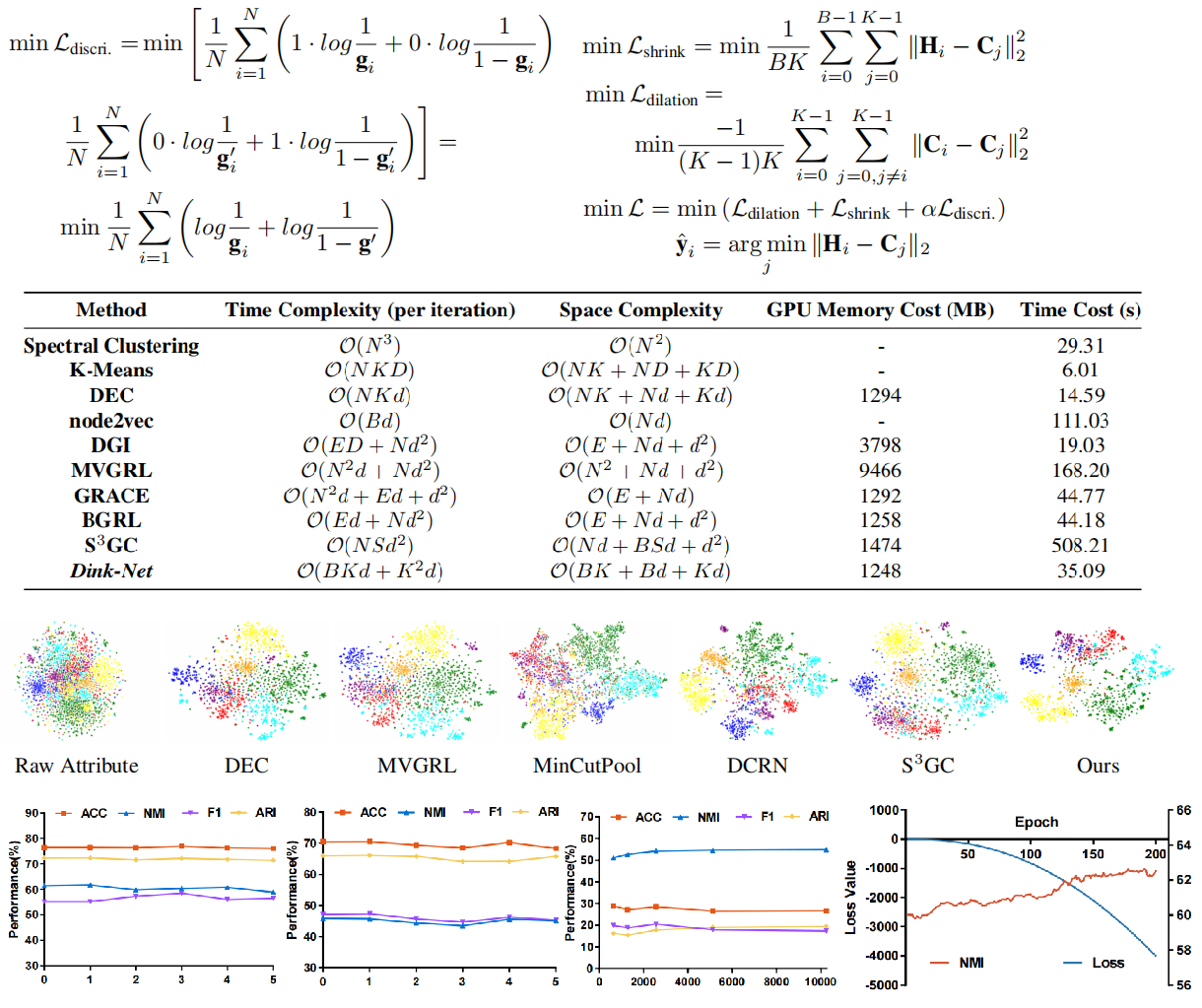
Yue Liu, K. Liang, Jun Xia, S. Zhou, X. Yang, Xinwang Liu, Stan Z. Li ICML, 2023 Paper / Code We analyze the drawbacks of existing deep graph clustering methods and scale deep graph clustering to large-scale graphs. The proposed shrink and dilation loss functions optimize clustering distribution adversarially, allowing batch training without performance dropping. |
|
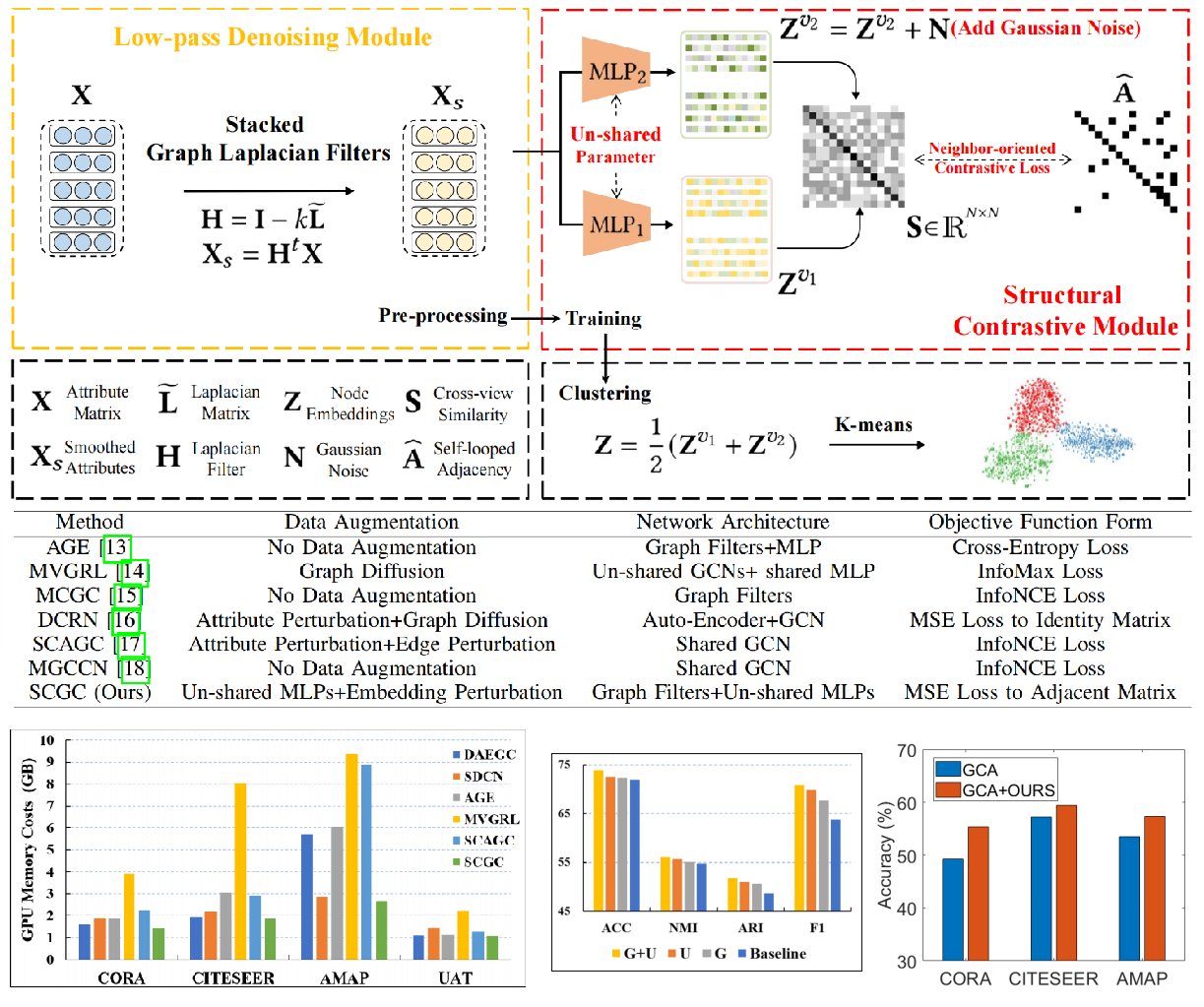
Yue Liu, X. Yang, S. Zhou, Xinwang Liu, S. Wang, K. Liang, W. Tu, L. Li, IEEE T-NNLS, 2023 Paper / Code We propose to replace the complicated and consuming graph data augmentations by designing parameter un-shared Siamese encoders and perturbing node embeddings. |
|
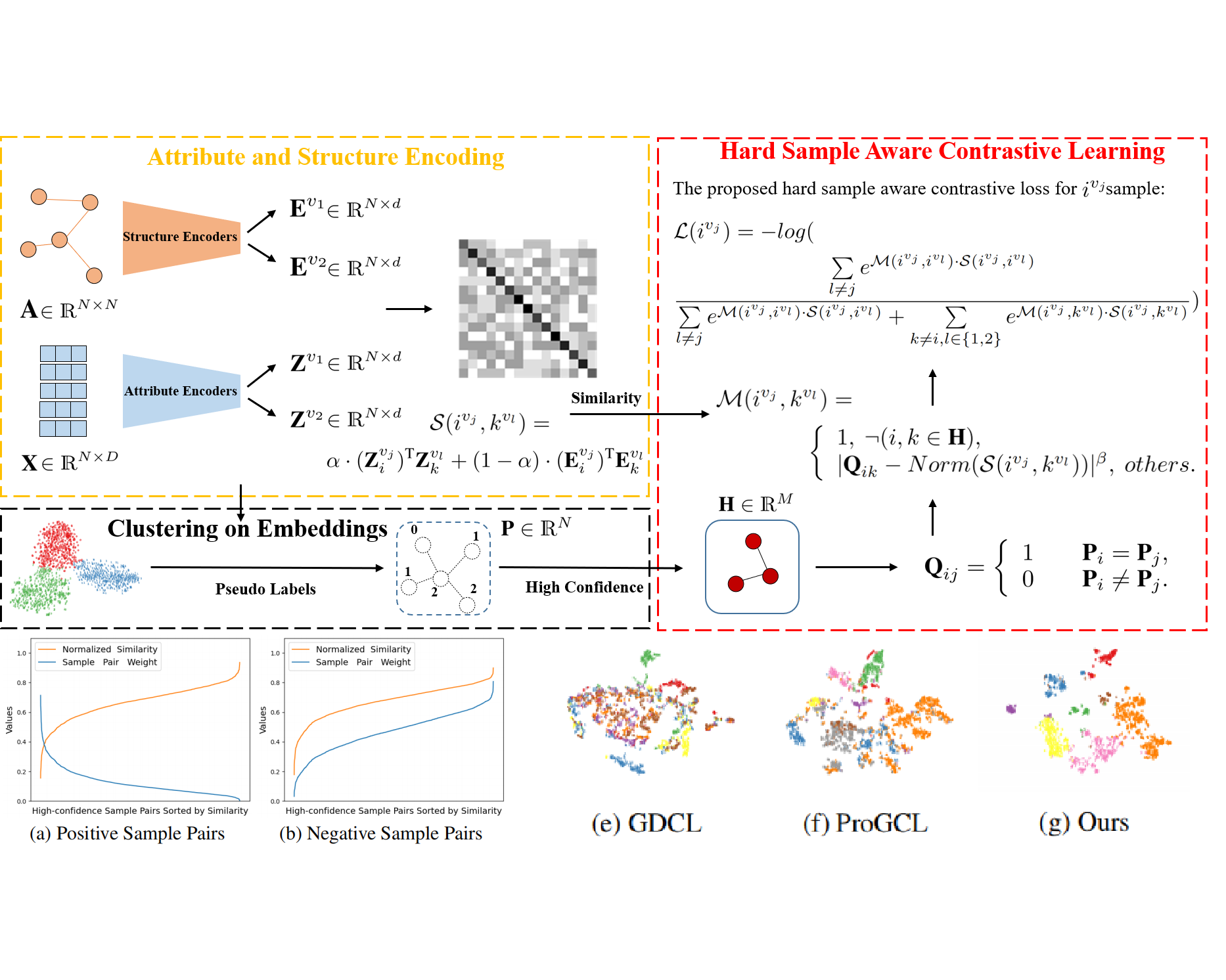
Yue Liu, X. Yang, S. Zhou, X. Liu, Z. Wang, K. Liang, W. Tu, L. Li, J. Duan, C. Chen AAAI (Oral & Most Influential AAAI Paper) (13/539) [Link], 2023 Paper / Code We propose a Hard Sample Aware Network (HSAN) to mine both the hard positive samples and hard negative samples with a comprehensive similarity measure criterion and a general dynamic sample weighing strategy. |
|
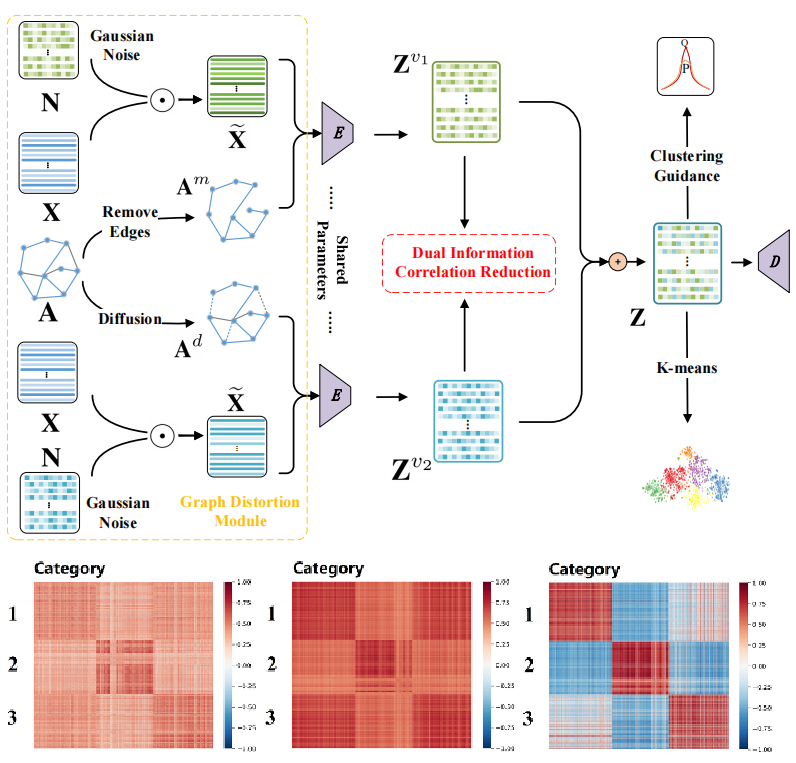
Yue Liu*, Wenxuan Tu*, S. Zhou, X. Liu, L. Song, X. Yang, E. Zhu AAAI, 2022 Paper / Code We propose a self-supervised deep graph clustering method termed Dual Correlation Reduction Network (DCRN) to address the representation collapse issue by reducing information correlation in both sample and feature levels. |
|
"If we knew what it was we were doing, it would not be called research, would it?" --Albert Einstein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website